Would you like to make this site your homepage? It's fast and easy...
Yes, Please make this my home page!
 |
Aquaponics
Library |
 |
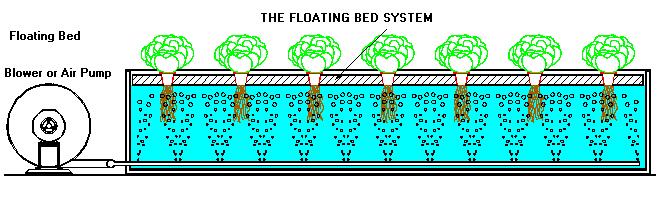
THE FLOATING BED SYSTEM
The simplest of all of the active systems is the floating bed
system.
In
it, the plants are anchoured in a floating platform placed
directly on the surface of the nutrient solution contained in a
container while the roots remain completly or partially submerged
in this solution.
It
is necessary to oxygenate the solution by bubbling air through an
air pump, a blower or even by recirculating the solution
periodically.
When
oxygenating the solution by bubbling air through it, this system
is considered a passive one.
However, as mentioned previously, oxygenation can be accomplished
by recirculating the solution by means of a pump, sometimes using
an air injector, in which case, this system is considered na
active one.
This
system is generally used for small plants that need very large
quantities of water, as is the case of lettuce, which produces
enormous productivity yelds when cultivated in the floating bed
system.
It
is also ideal for demonstrative purposes in schoolrooms where it
can be mounted using fish aquariuns.
The
biggest limitation is its inadequacy for medium and large sized
plants that have long life cycles.
When
cultivating larger plants it is common to attach the platform
over the sides of the solution container, in which case it
becomes known as the Fixed Bed System or Gerike's System.
It
is very commonly used with medium sized plants, such as tomatoes,
where an auxiliary structure is added in order to guide and
support the tomato plants.
Today, it is more commonly used in external domestic orchards, in
plant nutrition research labs and for school demonstrations.